|

CZECH LEGION ON A TRAIN IN SIBERIA
Russian History 1918
Russian
Civil War Timeline - Year 1918
|
|
Top Photo
Czechoslovak Legion and the Trans-Siberian Railway.
Source: marxists.org
|
January 10, 1918
(December 28, 1917
 old style)
old style)
The Cossacks declare their independence and form the
Republic of the Don.
January 12, 1918
(December 30, 1917
 old style)
old style)
The Latvians declare their independence from Russia but find it hard to celebrate
while occupying Germans are still
sitting on their laps.
January 18, 1918 (January
5, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The
Constituent Assembly gathers.
The
Bolsheviks demand that authority
should be given to the Soviets.
( What is a Soviet?) What is a Soviet?)
The Assembly refuses.
The Bolsheviks
and the  Left Socialist Revolutionaries walk out.
Left Socialist Revolutionaries walk out.
January 19, 1918 (January 6, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The
Bolshevik government sends troops to disperse the Constituent
Assembly. All non-Bolsheviks get a handbasket each and are told to
be gone.
January 22, 1918
(January 9, 1917
 old style)
old style)
The Ukrainians declare their
independence from Russia.
January 28, 1918
(January 15, 1917
 old style)
old style)
Civil War breaks out in Finland as a result of the recent Finnish
declaration of independence from Russia.
February 2, 1918 (January
20, 1918
 old style)
old style)
A new
ruling officially separates the Orthodox church from the state. Religious persecution
ensues. Church
property will get pillaged and churches destroyed.
February 9, 1918
(January
27, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Central Powers and the
Ukraine sign the
 Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
February 10, 1918
(January
28, 1918
 old style)
old style)
 Trotsky declares that Russia is
out of WWI.
Trotsky declares that Russia is
out of WWI.
February 11, 1918
(January 29, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Bolsheviks gain the upper hand against the Cossacks. Cossack
leader Aleksey Maksimovich Kaledin
shoots himself. Pyotr Nikolayevich Krasnov
will be his successor.
February 13, 1918
(January 31, 1918
 old style)
old style)
Calendar switch - Julian to Gregorian.
January 31, 1918 old style was
followed by February 14, 1918 new style. Some Russian locations
dragged their feet buying new calendars, so we will keep showing old
style dates a little while longer.
February 16, 1918
(February 3, 1918
 old style)
old style)
While still under German occupation, the Lithuanians declare their
independence from Russia.
February 18, 1918
(February 5, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Reds capture Kiev. They will stay in town until March 3, 1918,
when the Germans will knock on the doors.
February 24, 1918
(February 11, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Estonians declare their independence from Russia.
March 1918
(Mid-February - Mid-March, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Bolsheviks permit
the
 Czechoslovak Legion
to leave Russia via
Vladivostok.
Czechoslovak Legion
to leave Russia via
Vladivostok.
March 3, 1918
(February 18, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Red Army has to withdraw from Kiev because of incoming Germans.
The Germans let themselves in
because the Russians had just signed the
 Treaty
of Brest-Litovsk. Treaty
of Brest-Litovsk.
March 12, 1918
(February 27, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Bolsheviks move their capital from Petrograd to
Moscow for safety reasons.
March 13, 1918
(February 28, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Germans take Odessa.
March 17, 1918
(March 4, 1918
 old style)
old style)
The Germans take Nikolayev.
March 26, 1918
(March 13, 1918
 old style)
old style)
 Leon
Trotsky changes
office cubicles. He resigns his post as Foreign
Commissar and becomes the new War Commissar.
Georgy Vasilyevich
Chicherin takes Trotsky's old office chair and becomes
Foreign Commissar.
Leon
Trotsky changes
office cubicles. He resigns his post as Foreign
Commissar and becomes the new War Commissar.
Georgy Vasilyevich
Chicherin takes Trotsky's old office chair and becomes
Foreign Commissar.
Although the
 Red
Army had been already created in
January 1918, there is still a lot of work
to do. Trotsky whips the bunch into
shape and recruits many former
Red
Army had been already created in
January 1918, there is still a lot of work
to do. Trotsky whips the bunch into
shape and recruits many former
 Imperial
Army officers, some of which joined more voluntarily than others.
Imperial
Army officers, some of which joined more voluntarily than others.

LEON
TROTSKY POINTING IT OUT TO RED ARMY SOLDIERS
Source
Unknown
April 5,
1918
British and Japanese marines
land at Vladivostok.
April 8, 1918
The Germans take Kharkov and Rostov.
April 9, 1918
The Moldavian Republic and Romania declare their union. Russia is
against this union and feels Moldavia should belong to Russia.
April 10 - 13, 1918
Battle of Yekaterinodar.
April
13, 1918
 Kornilov gets killed. New
commander of the White Army is Anton
Ivanovich Denikin.
Kornilov gets killed. New
commander of the White Army is Anton
Ivanovich Denikin.
April 22, 1918
The Transcaucasians declare their independence from Russia and form
the Transcaucasian Republic. This Republic will dissolve on May 26,
1918.
May
1918
 Aleksandr Fyodorovich
Kerensky had remained in hiding until May 1918. Now he emigrates to
western Europe, writes books and edits revolutionary papers.
Aleksandr Fyodorovich
Kerensky had remained in hiding until May 1918. Now he emigrates to
western Europe, writes books and edits revolutionary papers.
May
1, 1918
The Germans take Sevastopol.
May
26, 1918
The Transcaucasian Republic splits into three separate states.
Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan declare their individual
independence from Russia.
May 29, 1918
 Leon
Trotsky, in his capacity of the commissar for war,
orders
the
Leon
Trotsky, in his capacity of the commissar for war,
orders
the
 Czechoslovak Legion
to
surrender their arms. The Legion refuses and takes control of
the Trans-Siberian railroad. Czechoslovak Legion
to
surrender their arms. The Legion refuses and takes control of
the Trans-Siberian railroad.
The U.S. declares itself sympathetic
to the goals of the Czech Legion.
June 7, 1918
(May 25, 1918
 old style)
old style)
Armed collision between the
 Red Army
and the
Red Army
and the
 Czech Legion at Chelyabinsk,
or Cheliabinsk, which is located
in west-central Russia. Here is
Chelyabinsk on a map.
Czech Legion at Chelyabinsk,
or Cheliabinsk, which is located
in west-central Russia. Here is
Chelyabinsk on a map.
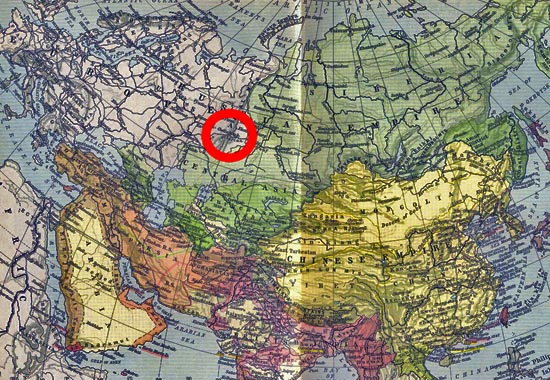
Map location of
Chelyabinsk, west central Russia
Click to view
original map of Asia (enlarged)
The
 Czechoslovak Legion
and the Socialist
Revolutionaries
form a government for the Volga, the Volga
Republic. Czechoslovak Legion
and the Socialist
Revolutionaries
form a government for the Volga, the Volga
Republic.
June 23, 1918
British troops land at Murmansk.
July 4 - 10, 1918
The Fifth All-Russian Congress of Soviets
commences.
The left Socialist Revolutionaries who had
previously participated in the Bolshevik government,
are now expelled.
Additional
happenings at the congress. The
1918 Constitution of the
Russian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic (RSFSR)
is adopted on July 10, 1918.
July 6, 1918
Disgruntled
 Left Socialist Revolutionaries
stage a revolt in Moscow.
Left Socialist Revolutionaries
stage a revolt in Moscow.
July 10, 1918
 Vatsetis
becomes commander of the Eastern Front.
Vatsetis
becomes commander of the Eastern Front.
Night of July 16 / 17, 1918
White forces and the Czech Legion come
dangerously close to Yekaterinburg.
Out of fear the former Tsar
 Nicholas II and his family might be liberated, the Bolsheviks
think it too
risky to keep the prisoners alive. So they shoot
the entire Imperial Family.
Nicholas II and his family might be liberated, the Bolsheviks
think it too
risky to keep the prisoners alive. So they shoot
the entire Imperial Family.
July
25, 1918
The Czech Legion captures Yekaterinburg.
August 2, 1918
British and French forces land at Arkhangelsk
(Archangel).
August
5 - 7, 1918
The
 Czech Legion together with the
Czech Legion together with the
 People's Army
take Kazan from the Reds, who were led by
People's Army
take Kazan from the Reds, who were led by
 Vatsetis.
Kazan opens the door to Moscow.
Vatsetis.
Kazan opens the door to Moscow.
August
8, 1918
Mamantov moves towards Tsaritsyn.
The
Siege of Tsaritsyn begins.
August
11, 1918
Japanese troops land at Vladivostok.
August 13, 1918
Battle of Sviiazhsk,
also called Sviyazhsk, on the eastern front,
which results in a decisive
 Red
Army victory over the
People's Army
of Komuch.
Red
Army victory over the
People's Army
of Komuch.
August
30, 1918
A female assassin,
Fanya Kaplan, also spelled Fanny
Kaplan, fires three bullets at
 Lenin as he
left a factory in which he had just delivered a
speech. Two bullets hit him, one in his jaw, one
in his shoulder. Lenin will recover.
Lenin as he
left a factory in which he had just delivered a
speech. Two bullets hit him, one in his jaw, one
in his shoulder. Lenin will recover.
Meanwhile in
Petrograd...
Leonid
Ioakimovich Kannegiser shoots
Moses Solomonovich
Uritsky, the Chairman of the Petrograd Cheka.
The two
assassinations are unrelated but the freakish
coincidence causes the Bolsheviks to run
around paranoid and angry while armed.
September 2, 1918
The Revolutionary
Military Council (Revvoensovet) is
created. This Council will function as the
executive board of the Red Army. In 1934, it
will be renamed to
Military Council.
The Bolshevik government proclaims a campaign
of Red Terror.
September 4, 1918
American troops join the British troops at
Murmansk.
September 5, 1918
Battle of Kazan
in which 11,000 Reds fight 6,000 Whites and
Czechs. This battle will end on September 10,
1918 with a victory for the Reds.
Japanese troops
take Khabarovsk.
September 6, 1918
 Colonel Vatsetis becomes Supreme
Commander-in-Chief of the Red forces.
Colonel Vatsetis becomes Supreme
Commander-in-Chief of the Red forces.
September 10, 1918
The Reds re-capture Kazan. The Battle of Kazan
had begun on September 5, 1918.
September 22, 1918
Second
Battle of Tsaritsyn.
This Battle will last until October 15, 1918.
September 23, 1918
A new government is created, the
Provisional
All-Russian Government, based at Omsk.
This
Siberian government, sponsored by the
 Komuch, will last until November 18,
1918, when
Komuch, will last until November 18,
1918, when
 Admiral Kolchak,
currently War Minister
in this government, will put an end to it.
Admiral Kolchak,
currently War Minister
in this government, will put an end to it.
October 7, 1918
The Reds take Samara.
October 14, 1918
The British reach Irkutsk.
October 15, 1918
End of the Second
Battle of Tsaritsyn. This Battle had started on September
22, 1918.
November 1, 1918
Poland declares war on the Ukraine.
November 4, 1918
The British occupy Mosul.
November 7, 1918
The Reds recapture Izhevsk.
November 11, 1918
Germany signs the
 WWI
Armistice.
WWI
Armistice.
November 15, 1918
The Ukrainians get a new government.
Simon Petliura succeeds
Pavel Skoropadski.
November
17, 1918
The British retake Baturn.
Karlis Ulmanis is
the new prime minister of Latvia.
November 18, 1918
 The Kolchak Coup
-
Coup d'état at Omsk.
The Kolchak Coup
-
Coup d'état at Omsk.
 Aleksandr
Vasilyevich Kolchak becomes the
leader of the White
Army, and supposed leader of entire
Russia, actually, because he sets up his own
government. Kolchak is now a military
dictator.
Aleksandr
Vasilyevich Kolchak becomes the
leader of the White
Army, and supposed leader of entire
Russia, actually, because he sets up his own
government. Kolchak is now a military
dictator.
Also on November 18,
1918 -
Latvia declares independence.
Also on November 18,
1918 -
Kolchak launches his Eastern Russia Offensive.
It will end on December 24, 1918.
November 22, 1918
The Germans withdraw from
Estonia and the Bolsheviks pour into the country.
November 23, 1918
Poland takes Lemberg.
November 27, 1918
Bessarabia announces its union with Romania.
Russia begs to differ.
December 8, 1918
Switzerland cuts diplomatic relations with
Soviet Russia.
December 18, 1918
Germany's defeat in WWI exposed the Black Sea to
the Allies.
French troops occupy Odessa to support the
Whites.
December 24, 1918
 Kolchak
captures Perm and Ufa.
Kolchak
captures Perm and Ufa.
More History
|