|

Napoleon Bonaparte in 1800
War of the Second Coalition
1798-1802
Also spelled
War of the 2nd
Coalition, this war was part of the
 French
Revolutionary Wars.
French
Revolutionary Wars.
|
|
Who Fought the War of the Second Coalition?
France
against
the Second
Coalition
(Britain, Austria, Russia, the Ottoman
Empire, Naples, and Portugal)
Check here for the various
 Coalitions
that were formed to fight against France.
Coalitions
that were formed to fight against France.
Image Above
In front: Napoleon Bonaparte as
First Consul, shortly after the Battle of Marengo on June 14, 1800. Oil on canvas by
Andrea Appiani, who lived 1754-1817.
Christie's auctioned this painting
with an estimated $150,000. On June 17, 2004, it sold for $769,100.
And Christie's tells us more:
This uniform, known as the Marengo uniform, is today part
of the collection of the Musée des Invalides, Paris, where it is
on display in the Salle Consulat.
The
uniform and the sabre were specifically requested by
Jacques-Louis David, when, at the end of 1800, he painted the
famous equestrian portrait of Bonaparte crossing the Alps at the
Grand-Saint-Bernard pass.
|
When Did the War of the Second Coalition
Begin?
The War of the Second Coalition begun
on November 29, 1798, when
 Karl Mack
led an army of 40,000 Neapolitan troops into Rome, thus seriously
challenging the recently installed French
Karl Mack
led an army of 40,000 Neapolitan troops into Rome, thus seriously
challenging the recently installed French
 Roman
Republic.
Roman
Republic.
Check this event in the
 Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Although their commander, Karl Mack,
was Austrian, the army that entered Rome was not a coalition force. It was the army of the
 Kingdom of Naples (Kingdom of
the Two Sicilies.)
Kingdom of Naples (Kingdom of
the Two Sicilies.)
Why, then, can this event be referred to as the starting point of
the War of the Second Coalition?
Because by this time, the Second Coalition had already
formed. Although it had not
yet been completely consolidated, the rest was only paper work.
In fact, one of the reasons for Naples'
premature campaign had been pressure from Britain to become more active
against the French. And in turn, by this move, Naples was applying
pressure on Austria to do the same.
Members of the Second
Coalition Already at War With France
On November 29, 1798, the following members of the
Second Coalition were already at war with France:
:: Britain
Britain
had been at war with France without interruption since 1793.
:: Portugal
Technically,
Portugal was also still at war with France because it
never signed a peace treaty after the
 War of the First Coalition.
Portugal had become an ally in 1793 when it assisted Britain and
Spain with troops on land and sea.
War of the First Coalition.
Portugal had become an ally in 1793 when it assisted Britain and
Spain with troops on land and sea.
:: Ottoman Empire
Prodded by Napoleon's
 Egyptian Campaign, the
Ottoman Empire had declared war
on France on September 11, 1798.
Egyptian Campaign, the
Ottoman Empire had declared war
on France on September 11, 1798.
When Did the War of the Second Coalition
End?
The War of the Second Coalition ended
on March 27, 1802, when the
 Treaty of Amiens
was signed. Treaty of Amiens
was signed.
Check this event in the
 Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Timeline of the French Revolutionary Wars.
Who Won the War of the Second Coalition?
Who Lost?
France was the victor of the War of
the Second Coalition.
The Second Coalition lost mainly due
to the fact that its members couldn't agree on a joint strategy
against France.
What Was the Main
Difference Between the First and the Second Coalition?
In the
 First Coalition, Prussia was
in, and Russia was out.
First Coalition, Prussia was
in, and Russia was out.
In the Second Coalition, Prussia was
out, and Russia was in.
:: Prussia
Prussia was a sought-after ally by the
members of the Second Coalition. In fact,
Russia was prepared to furnish Prussia with 45,000 troops, for which Britain was prepared to pick up the tab. But Prussia's new king,
 Frederick William III, decided
to take a time-out. He rejoined the fight against France in the Frederick William III, decided
to take a time-out. He rejoined the fight against France in the
 War of the Fourth Coalition. Of
course, by then it was too late.
War of the Fourth Coalition. Of
course, by then it was too late.
:: Russia
Russia's new sovereign was
 Paul I, a man whom
the very competent
Paul I, a man whom
the very competent
 Catherine the Great tried to
keep away from the throne, even though it was her son. Paul ruled
1796-1801. Catherine the Great tried to
keep away from the throne, even though it was her son. Paul ruled
1796-1801.
What Were the Main
Treaties Behind the Second Coalition?
May 19, 1798
Treaty concluded at
Vienna between Austria and the
Two Sicilies (Naples)
November 29, 1798
Treaty concluded
at Saint Petersburg between Russia and the
Two Sicilies
December 1, 1798
Treaty concluded at
Naples between Britain and the
Two Sicilies
December 25, 1798
Treaty concluded
at Constantinople between Russia and the
Ottoman Empire
December 29, 1798
Treaty concluded
at Saint Petersburg between Russia and
Britain
January 2, 1799
Treaty concluded at
Constantinople between Britain and the
Ottoman Empire
January 21, 1799
Treaty concluded at
Constantinople between the Ottoman Empire and the
Two Sicilies
September 28, 1799
Treaty concluded
at Saint Petersburg between Russia and
Portugal
October 1, 1799
Treaty concluded
between Russia and
Bavaria
March 16, 1800
Treaty concluded at
Munich between Britain and
Bavaria
April 20, 1800
Treaty concluded at
Louisburg between Britain and
Wurttemberg (Württemberg)
April 30, 1800
Treaty concluded
between Britain and
Mayence (Mainz)
June 20, 1800
Treaty between
Britain and
Austria
Brief Timeline, Key Events and
Battles of the War of the Second Coalition
November 29, 1798 - Naples evicts the
French from Rome
December 4, 1798 -
 Battle of Civita Castellana
Battle of Civita Castellana
March 12, 1799
- France declares war on Austria
March 25, 1799
-
 Battle of Stokach
Battle of Stokach
April 27, 1799
-
 Battle of Cassano
Battle of Cassano
June 4-6, 1799 -
 First Battle of Zurich
First Battle of Zurich
June 17-19,
1799 -
 Battle of Trebbia
Battle of Trebbia
August 15,
1799 -
 Battle of Novi
Battle of Novi
September 25-26, 1799 -
 Second Battle of Zurich
Second Battle of Zurich
April 21 -
June 4, 1800 -
 Siege of Genoa
Siege of Genoa
June 14, 1800 -
 Battle of Marengo
Battle of Marengo
December 3, 1800 -
 Battle of
Hohenlinden
Battle of
Hohenlinden
April 2, 1801
-
 Battle of Copenhagen
Battle of Copenhagen
March 27, 1802 -
 Treaty of Amiens
Treaty of Amiens
More detailed timelines here:
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1798
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1798
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1799
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1799
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1800
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1800
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1801
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1801
 French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1802
French Revolutionary
Wars Timeline - 1802
And here are the maps
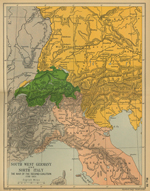
Map of the War of the Second Coalition 1798-1801
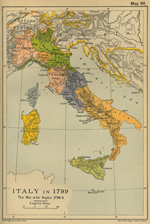
1799 Italy
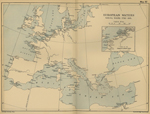
1792-1815
European Waters
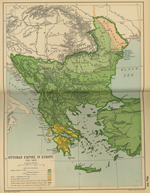
1792 Ottoman Empire in Europe
More History
|