|
Second Battle of Saratoga — October
7, 1777
The Second Battle of Saratoga was
also called the
Second
Battle of Freeman's Farm
or the
Battle of Bemis Heights.
---> Quoted from The
Fifteen Decisive Battles of the World by Edward S. Creasy
THE SECOND BATTLE OF SARATOGA
It was on the 7th of October that Burgoyne led his column forward.
And on the preceding day, the 6th, Clinton had successfully executed
a brilliant enterprise against the two American forts which barred
his progress up the Hudson.
He had captured them both, with severe
loss to the American forces opposed to him. He had destroyed the
fleet which the Americans had been forming on the Hudson, under the
protection of their forts. And the upward river was laid open to his
squadron. He had also, with admirable skill and industry, collected
in small vessels, such as could float within a few miles of Albany,
provisions sufficient to supply Burgoyne's army for six months.
He was now only a hundred and fifty-six
miles distant from Burgoyne. And a detachment of 1,700 men actually
advanced within forty miles of Albany. Unfortunately, Burgoyne and
Clinton were each ignorant of the other's movements. But if Burgoyne
had won his battle on the 7th, he must on advancing have soon
learned the tidings of Clinton's success, and Clinton would have
heard of his.
A junction would soon have been made of
the two victorious armies, and the great objects of the campaign
might yet have been accomplished. All depended on the fortune of the
column with which Burgoyne on the eventful 7th October 1777,
advanced against the American position.
There were brave men, both English and
German, in its ranks. And in particular it comprised one of the best
bodies of grenadiers in the British service.
Burgoyne pushed forward some bodies of
irregular troops to distract the enemy's attention. And led his
column to within three quarters of a mile from the left of Gates'
camp and then deployed his men into line. The grenadiers under Major
Ackland, and the artillery under Major Williams, were drawn up on
the left.
A corps of Germans, under General
Reidesel, and some British troops under General Phillips, were in
the center. And the English Light Infantry, and the 24th regiment,
under Lord Balcarres and General Frazer, were on the right.
But Gates did not wait to be attacked,
and directly the British line was formed and began to advance the
American general, with admirable skill, caused General Poor's
brigade of New York and New Hampshire troops, and part of General
Leonard's brigade, to make a sudden and vehement rush against its
left, and at the same time sent Colonel Morgan, with his rifle corps
and other troops, amounting to 1,500, to turn the right of the
English.
The grenadiers under Ackland sustained
the charge of superior numbers nobly. But Gates sent more Americans
forward, and in a few minutes the action became general along the
center, so as to prevent the Germans from detaching any help to the
grenadiers.
Morgan, with his riflemen, was now
pressing Lord Balcarres and General Frazer hard, and fresh masses of
the enemy were observed advancing from their extreme left, with the
evident intention of forcing the British right, and cutting off its
retreat.
The English Light Infantry and the 24th
now fell back, and formed an oblique second line, which enabled them
to baffle this maneuver and also to succor their comrades in the
left wing, the gallant grenadiers, who were overpowered by superior
numbers, and, but for this aid, must have been cut to pieces.
The contest now was fiercely maintained
on both sides. The English cannon were repeatedly taken and retaken.
But when the grenadiers near them were forced back by the weight of
superior numbers, one of the guns was permanently captured by the
Americans and turned upon the English.
Major Williams and Major Ackland were
both made prisoners, and in this part of the field the advantage of
the Americans was decided. The British center still held its ground
but now it was that the American general Arnold appeared upon the
scene, and did more for his countrymen than whole battalions could
have effected.
Arnold, when the decisive engagement of
the 7th of October commenced, had been deprived of his command by
Gates, in consequence of a quarrel between them about the action of
the 19th of September.
He had listened for a short time in the
American camp to the thunder of the battle, in which he had no
military right to take part, either as commander or as combatant.
But his excited spirit could not long endure such a state of
inaction. He called for his horse, a powerful brown charger, and
springing on it, galloped furiously to where the fight seemed to be
the thickest.
Gates saw him, and sent an aide-de-camp
to recall him. But Arnold spurred far in advance and placed himself
at the head of three regiments which had formerly been under him,
and which welcomed their old commander with joyous cheers.
He led them instantly upon the British
center and then galloping along the American line, he issued orders
for a renewed and a closer attack, which were obeyed with alacrity,
Arnold himself setting the example of the most daring personal
bravery, and charging more than once, sword in hand, into the
English ranks.
On the British side the officers did
their duty nobly. But General Frazer was the most eminent of them
all, restoring order wherever the line began to waver, and infusing
fresh courage into his men by voice and example. Mounted on an
iron-grey charger, and dressed in the full uniform of a general
officer, he was conspicuous to foes as well as to friends.
The American Colonel Morgan thought that
the fate of the battle rested on this gallant man's life, and
calling several of his best marksmen round him, pointed Frazer out,
and said, "That officer is General Frazer. I admire him but he must
die. Our victory depends on it. Take your stations in that clump of
bushes and do your duty." Within five minutes Frazer fell mortally
wounded and was carried to the British camp by two grenadiers.
Just previously to his being struck by
the fatal bullet, one rifle-ball had cut the crupper of his saddle,
and another had passed through his horse's mane close behind the
ears. His aide-de-camp had noticed this, and said, "It is evident
that you are marked out for particular aim. Would it not be prudent
for you to retire from this place?"
Frazer replied, "My duty forbids me to
fly from danger." And the next moment he fell.
Burgoyne's whole force was now compelled
to retreat towards their camp. The left and center were in complete
disorder but the light infantry and the 24th checked the fury of the
assailants, and the remains of the column with great difficulty
effected their return to their camp, leaving six of their cannons in
the possession of the enemy and great numbers of killed and wounded
on the field. And especially a large proportion of the artillerymen,
who had stood to their guns until shot down or bayoneted beside them
by the advancing Americans.
Burgoyne's column had been defeated, but
the action was not yet over. The English had scarcely entered the
camp, when the Americans, pursuing their success, assaulted it in
several places with remarkable impetuosity, rushing in upon the
entrenchments and redoubts through a severe fire of grape-shot and
musketry.
Arnold especially, who on this day
appeared maddened with the thirst of combat and carnage, urged on
the attack against a part of the entrenchments which was occupied by
the light infantry under Lord Balcarres.
But the English received him with vigor
and spirit. The struggle here was obstinate and sanguinary. At
length, as it grew towards evening, Arnold, having forced all
obstacles, entered the works with some of the most fearless of his
followers. But in this critical moment of glory and danger, he
received a painful wound in the same leg which had already been
injured at the assault on Quebec.
To his bitter regret he was obliged to
be carried back. His party still continued the attack, but the
English also continued their obstinate resistance, and at last night
fell, and the assailants withdrew from this quarter of the British
entrenchments.
But in another part the attack had been
more successful. A body of the Americans, under Colonel Brooke,
forced their way in through a part of the horse-shoe entrenchments
on the extreme right, which was defended by the Hessian reserve
under Colonel Breyman. The Germans resisted well, and Breyman died
in defense of his post. But the Americans made good the ground which
they had won and captured baggage, tents, artillery, and a store of
ammunition, which they were greatly in need of.
They had, by establishing themselves on
this point, acquired the means of completely turning the right flank
of the British, and gaining their rear.
To prevent this calamity, Burgoyne
effected during the night an entire change of position. With great
skill he removed his whole army to some heights near the river, a
little northward of the former camp, and he there drew up his men,
expected to be attacked on the following day.
But Gates was resolved not to risk the
certain triumph which his success had already secured for him. He
harassed the English with skirmishes, but attempted no regular
attack.
Meanwhile he detached bodies of troops
on both sides of the Hudson to prevent the British from re-crossing
that river, and to bar their retreat.
When night fell it became absolutely
necessary for Burgoyne to retire again, and accordingly the troops
were marched through a stormy and rainy night towards Saratoga,
abandoning their sick and wounded, and the greater part of their
baggage, to the enemy.
Before the rear-guard quitted the camp,
the last sad honors were paid to the brave General Frazer, who
expired on the day after the action.
He had, almost with his last breath,
expressed a wish to be buried in the redoubt which had formed the
part of the British lines where he had been stationed but which had
now been abandoned by the English, and was within full range of the
cannon which the advancing Americans were rapidly placing in
position to bear upon Burgoyne's force.
Burgoyne resolved, nevertheless to
comply with the dying wish of his comrade and the interment took
place under circumstances the most affecting that have ever marked a
soldier's funeral.
Still more interesting is the narrative
of Lady Ackland's passage from the British to the American camp,
after the battle, to share the captivity and alleviate the
sufferings of her husband, who had been severely wounded, and left
in the enemy's power.
The American historian Lossing,
has described both these touching episodes of the campaign, in a
spirit that does honor to the writer as well as to his subject.
After narrating the death of General Frazer on the 8th of October,
he says that "It was just at sunset, on that calm October evening,
that the corpse of General Frazer was carried up the hill to the
place of burial within the 'great redoubt'. It was attended only by
the military members of his family and Mr. Brudenell, the chaplain.
Yet the yes of hundreds of both armies followed the solemn
procession, while the Americans, ignorant of its true character,
kept up a constant cannonade upon the redoubt.
The chaplain, unawed by the danger to
which he was exposed, as the cannon balls that struck the hill threw
the loose soil over him, pronounced the impressive funeral service
of the Church of England with an unfaltering voice. The growing
darkness added solemnity to the scene.
Suddenly the irregular firing ceased,
and the solemn voice of a single cannon, at measured intervals,
boomed along the valley, and awakened the responses of the hills.
It was a minute gun fired by the
Americans in honor of the gallant dead. The moment the information
was given that the gathering at the redoubt was a funeral company,
fulfilling, at imminent peril, the last breathed wishes of the noble
Frazer, orders were issued to withhold the cannonade with balls, and
to render military homage to the fallen brave.
The case of Major Ackland and his heroic
wife presents kindred features. He belonged to the grenadiers, and
was an accomplished soldier. His wife accompanied him to Canada in
1776 and during the whole campaign of that year, and until his
return to England after the surrender of Burgoyne, in the autumn of
1777, endured all the hardships, dangers, and privations of an
active campaign in an enemy's country.
At Chambly, on the Sorel, she attended
him in illness, in a miserable hut and when he was wounded in the
Battle of Hubbardton, Vermont, she hastened to him at
Henesborough from Montreal, where she had been persuaded to remain,
and resolved to follow the army hereafter.
Just before crossing the Hudson, she and
her husband had had a narrow escape from losing their lives in
consequence of their tent accidentally taking fire.
During the terrible engagement of the
7th October, she heard all the tumult and dreadful thunder of the
battle in which her husband was engaged. And when on the morning of
the 8th the British fell back in confusion to their new position,
she with the other women, was obliged to take refuge among the dead
and dying, for the tents were all struck, and hardly a shed was left
standing.
Her husband was wounded and a prisoner
in the American camp. That gallant officer was shot through both
legs. When Poor and Leonard's troops assaulted the grenadiers and
artillery on the British left, on the afternoon of the 7th,
Wilkinson, Gates' adjutant-general, while pursuing the flying
enemy when they abandoned their battery, heard a feeble voice
exclaim 'Protect me, sir, against that boy.'
He turned and saw a lad with a musket
taking deliberate aim at a wounded British officer, lying in a
corner of a low fence. Wilkinson ordered the boy to desist, and
discovered the wounded man to be Major Ackland. He had him conveyed
to the quarters of General Poor (now the residence of Mr. Neilson)
on the heights, where every attention was paid to his wants.
When the intelligence that he was
wounded and a prisoner reached his wife, she was greatly distressed,
and by the advice of her friend, Baroness Reidesel, resolved to
visit the American camp, and implore the favor of a personal
attendance upon her husband. On the 9th she sent a message to
Burgoyne by Lord Petersham, his aide-de-camp, asking permission to
depart.
"Though I was ready to believe" says
Burgoyne, "that patience and fortitude, in a supreme degree, were to
be found, as well as every other virtue, under the most tender
forms, I was astonished at this proposal. After so long an agitation
of spirits, exhausted not only for want of rest, but absolutely want
of food, drenched in rains for twelve hours together, that a woman
should be capable of such an undertaking as delivering herself to an
enemy, probably in the night, and uncertain of what hands she might
fall into, appeared an effort above human nature. The assistance I
was able to give was small indeed. I had not even a cup of wine to
offer her. All I could furnish her with was an open boat, and a few
lines, written upon dirty wet paper, to General Gates, recommending
her to his protection."
[...]
In the morning she experienced parental
tenderness from General Gates, who sent her to her husband, at
Poor's quarters, under a suitable escort. There she remained until
he was removed to Albany.
Burgoyne now took up his last position
on the heights near Saratoga and hemmed in by the enemy, who refused
any encounter and vaffled in all his attempts at finding a path of
escape, he there lingered until famine compelled him to capitulate.
[...]
At length the 13th of October arrived,
and as no prospect of assistance appeared, and the provisions were
nearly exhausted, Burgoyne, by the unanimous advice of a council of
war, sent a messenger to the American camp to treat of a convention.
[...]
Accordingly, on the 17th, the convention
of Saratoga was carried into effect. By this convention 5,790 men
surrendered themselves as prisoners. The sick and wounded left in
the camp when the British retreated to Saratoga, together with the
numbers of the British, German, and Canadian troops, who were
killed, wounded, or taken, and who had deserted in the preceding
part of the expedition, were reckoned to be 4,689.
---> End quote.
Go to the
 First Battle of Saratoga.
First Battle of Saratoga.
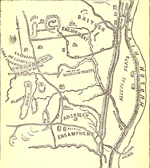
1777 Battle
of Saratoga
More History
|