|

Forms of Governments A-Z
Here
follows in a nutshell and
alphabetically a list of the various systems
of
government, their definition, origin of the
word, and examples in history.
|
|
Image Above
1999 Map of World
Governments
National
Constitution Center |
What's the
Definition of Government?
A system according to which a
nation, state, or community is administered, regulated, and
governed.
From Latin gubernare =
to direct, rule, guide, govern
If a sovereign oppresses his people to a
great degree, they will rise and cut off his
head. There is a remedy in human nature
against tyranny, that will keep us safe
under every form of government.
Samuel Johnson
in James Boswell's The Life of Samuel
Johnson, 1791
|
Absolutism |
| |
Absolute and unlimited government
exercised by a monarch, despot, or
dictator. The ruler answers to God
alone. And that only on a rainy day.
Arguably one of the best examples of absolutism was the
French monarch
 Louis XIV.
Another example of absolutism was Louis XIV.
Another example of absolutism was
 Adolf Hitler.
Adolf Hitler. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Autocracy |
| |
Absolute government.
Supreme, self-sustained, independent
[political] power.
Origin of the Word autocracy
From Greek
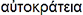 = autokrateia = ruling by oneself.
= autokrateia = ruling by oneself.
From auto = self,
one's own, by oneself, independently,
and krateia = might,
power, authority
Examples of Autocracies in
History
Classical autocracy can be studied
in the case of
 Nicholas I,
the Russian emperor from 1825 to
1855. He gave direct orders,
expected absolute obedience, and
there was no one who ruled the
country but him.
Nicholas I,
the Russian emperor from 1825 to
1855. He gave direct orders,
expected absolute obedience, and
there was no one who ruled the
country but him.
If
you're Catholic, you believe that
the Pope has supreme power over all
matters of faith and moral. Thus,
his is a case of religious
autocracy. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Anarchy |
| |
Absence of government.
No authority, no government, no
ruler.
Anarchism, then, really, stands
for the liberation of the human
mind from the dominion of
religion; the liberation of the
human body from the dominion of
property; liberation from the
shackles and restraints of
government.
Emma Goldman, 1910
Origin of the Word anarchy
From Greek
 = anarkhia = lack of a
leader, the state of people without
a government
= anarkhia = lack of a
leader, the state of people without
a government
From an =
without, and arkhos =
leader
Examples of Anarchies in History
Historians regard twenty years in
the history of the United Kingdom as
a period of anarchy. These were the
years from 1135 to 1154. Although
there were rulers, their rule was
disputed and as a result civil disturbances
followed.
Similarly, the word anarchy is used to
describe the general situation at
Athens, after the Spartans had introduced
the Thirty Tyrants as Athens' government in
404 BC. Although there was a
government it was not accepted as
such and civil unrest ensued.
This, however, is not the political
situation anarchists refer to.
Anarchy, as political philosophy, is
a theoretical social state in which
there is no governing person or body
of persons, but each individual has
absolute liberty, without
implication of disorder.
See
more under
 Communism -
What is Anarchism.
Communism -
What is Anarchism. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Communism |
| |
Social
system based on collective
ownership.
China
is a communist state, for example.
See
more under
 What is
Communism?
What is
Communism? |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Confederation |
| |
Alliance of political powers.
A bond or connection between
families, states, parties, or
individuals for certain common
purposes.
Origin of the Word confederation
From Latin confoederare =
to unite by a league
From com = with,
together, and foederare,
from foedus (gen. foederis)
= a league
Examples of Confederations in History
The Aetolian League and the Achaean
League in ancient Greece are
examples of confederations in
history.
See
more under
 Ancient Greeks.
Ancient Greeks.
After the
 Holy Roman
Empire had collapsed
in 1806, Germany was re-organized as
the
Holy Roman
Empire had collapsed
in 1806, Germany was re-organized as
the
 German
Confederation, just
to hold something together.
German
Confederation, just
to hold something together.
The
 Confederate
States of America
existed from 1861 to 1865.
Confederate
States of America
existed from 1861 to 1865. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Democracy |
| |
Government by the people.
Form of government in which the sovereign power resides in
the people as a whole, and is exercised either directly by
them (direct democracy) or by officers elected by them.
Democracy means government by
discussion, but it is only
effective if you can stop people
talking.
Clement Attlee, 1957
Origin of the Word democracy
From Greek
 = demokratia - popular government.
= demokratia - popular government.
From demos = the commons,
the people, and kratos
= rule, sway, authority.
Examples of Democracies in History
Although slavery was common in
ancient Athens, this city-state had a
democratic form of government.
See
more under
 Ancient Greeks
- Democracy
Ancient Greeks
- Democracy |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Despotism |
| |
or
Despotocracy: The rule of a despot.
Any ruler who governs absolutely or
tyrannically.
Origin of the Word despotism
From Greek
 = despotis = master, lord,
despot
= despotis = master, lord,
despot
Examples of Despotism in History
Despotism usually carries a negative
meaning. But not always. There were
also the "enlightened despots," such
as
 Frederick II
the Great,
Frederick II
the Great,
 Peter
I the Great, Peter
I the Great,
 Catherine II
the Great, and
Catherine II
the Great, and
 Maria Theresa
for example.
Maria Theresa
for example. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Dictatorship |
| |
or
dictatorialism, dictatory, dictature:
Ruled by a dictator or, in case of a
female dictator, dictatrix.
Dictator - one who has absolute
power or authority.
Dictators ride to and fro upon
tigers which they dare not
dismount. And the tigers are
getting hungry.
Sir Winston Churchill, 1937
Origin of the Word dictator
From Latin dicto / dictare =
to dictate, say, tell, remind,
suggest
In this context = To
prescribe a course or object of
action, To lay down authoritatively,
To order, or command in express
terms
Examples of Dictatorship in History
In
the
 Roman Republic
a dictator was appointed in times of
great crisis. Once the crisis had
been overcome, the dictator laid
down his dictatorship. One of these
dictators,
Quintus Hortensius, was
appointed in 287 BC to end the
struggle between plebeians and
patricians.
Roman Republic
a dictator was appointed in times of
great crisis. Once the crisis had
been overcome, the dictator laid
down his dictatorship. One of these
dictators,
Quintus Hortensius, was
appointed in 287 BC to end the
struggle between plebeians and
patricians.
 Julius Caesar
was dictator from 46 to 44 BC.
Julius Caesar
was dictator from 46 to 44 BC.
In
modern history, the word dictator
carries a negative vibe.
 Porfirio Diaz'
dictatorship in Mexico was called
the
Porfiriato.
Porfirio Diaz'
dictatorship in Mexico was called
the
Porfiriato.
 Adolf Hitler
added a new dimension to the term dictator.
Adolf Hitler
added a new dimension to the term dictator.
Other dictators in recent
history were
 Benito
Mussolini of Italy,
Enrique
Peralta Azurdia of
Guatemala, or
Nicolae Ceausescu of
Romania. Unfortunately, this list is by
no means exhaustive.
Benito
Mussolini of Italy,
Enrique
Peralta Azurdia of
Guatemala, or
Nicolae Ceausescu of
Romania. Unfortunately, this list is by
no means exhaustive. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Empire |
| |
Rule
or territory of an emperor or
empress.
Origin of the Word empire
From Latin imperium = rule,
command,
and from imperare = to
command
Examples of Emperors and Empires in History
In
the
 Roman Republic,
a very successful general could
become imperator.
Roman Republic,
a very successful general could
become imperator.
 Julius Caesar
was one of them. However, he was
never emperor of an empire, only
dictator of a republic.
Julius Caesar
was one of them. However, he was
never emperor of an empire, only
dictator of a republic.
Confused?
The
Emperor Penguin can grow up to 50
inches or 130 cm and has absolutely
nothing to do with this.
In
the
 Roman Empire,
the rulers adopted the proper name
Caesar as part of their
title. The title caesar
developed into the German word
kaiser and the Russian word
tsar, or czar.
Roman Empire,
the rulers adopted the proper name
Caesar as part of their
title. The title caesar
developed into the German word
kaiser and the Russian word
tsar, or czar.
 Kaiser Wilhelm
II (William II) was
Germany's last emperor.
Kaiser Wilhelm
II (William II) was
Germany's last emperor.
 Tsar Nicholas
II was Russia's last
emperor.
Tsar Nicholas
II was Russia's last
emperor. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Fascism |
| |
A
right-wing authoritarian system.
See
more under
 What is
Fascism?
What is
Fascism? |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Federation |
| |
A
political entity formed by a number
of separate states, each retaining
control of its own internal affairs.
Origin of the Word federation
From Latin foederare = league together,
and from foedus = covenant, league,
hence = union by agreement
Examples of Federations in History
Russia is a federation, and so is
Canada.
The
United States Constitution sets up a
federal system of government. Each
one of the 50 state governments has
their own governor and their own
constitution, as well as extensive
authority. But coining money, for
instance, is reserved for the
federal, also called national,
government. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Feudalism |
| |
A lord
owns land or property, and lets his
vassals or tenants use it in return
for service, e.g. military or
financially.
Origin of the Word feudal
From
Latin feudum = fief or
fee
Examples of Feudalism in History
The feudal
system could be found in Europe from
about the 5th to the 15th century.
 Magna Carta
regulated feudal law.
Magna Carta
regulated feudal law.
Here's a map
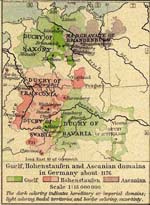
1176 Germany |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Monarchy |
| |
Governed by a monarch, i.e. a king,
queen, emperor, or empress.
Origin of the Word monarchy
From Greek
 = monarkhia = rule of one
= monarkhia = rule of one
From monos = alone and
arkhein = to rule
Examples of Monarchies in History
Back
in the days, a monarch was the sole
ruler of a state with absolute
power.
In
case of a constitutional monarchy,
the monarch has to share powers with
a constitutionally organized
government.
Constitutional monarchies today are
set up for example in Belgium, Britain,
Cambodia, Canada, Jordan, the Netherlands,
Norway, Spain, Sweden, and Thailand. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Oligarchy |
| |
Government by the few.
Authority is confined to a small,
elite group.
Origin of the Word oligarchy
From
Greek
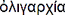 = oligarkhia = government by the
few
= oligarkhia = government by the
few
From oligoi = few, small,
little, and arkhein =
to rule
Examples of Oligarchies in History
Whenever there is a bunch of people
with concentrated wealth and power,
these guys usually try to defend and
protect their privileges. If they
become rulers, or oligarchs, their
rule can, but doesn't necessarily
have to be, detrimental.
Due to
controversy regarding the exact
definition and application of the
term, it is difficult to list
examples of oligarchies in history. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Republic |
| |
A
state in which supreme power rests
in the people through their elected
representatives, as opposed to a
state with a hereditary line of
leadership.
Origin of the Word republic
From
Latin respublica = public
interest, the state
From res = affair, matter,
thing, and publica =
public
Examples of Republics in History
Today,
the world's smallest republic is the
Republic of Nauru in the Pacific
Ocean, with 21 square kilometers or
8 square miles.
According to the CIA's World
Factbook, the United States has a
constitution-based federal republic
with a strong democratic tradition.
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Totalitarianism |
| |
A
system of government which tolerates
only one political party.
Totalitarian governments demand the
complete subservience of the
individual to the State, there is no
individual freedom.
Origin of the Word
totalitarianism
Mussolini coined the term. Hence,
from Italian totalitario = complete, absolute,
total
Examples of Totalitarianism in History
 Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Party: Nazi Party
In full: Nationalsozialistische
Deutsche Arbeiterpartei
(National Socialist German Workers'
Party)
 Benito
Mussolini
Benito
Mussolini
Party:
PNF
In full: Partito Nazionale Fascista
(National Fascist Party)
 Josef Stalin
Josef Stalin
Party:
CPSU
In full: Kommunisticheskaya Partiya
Sovetskogo Soyuza
(Communist Party of the Soviet
Union) |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Tyranny |
| |
An
absolute or despotic government.
The rule of a tyrant or tyranness.
Origin of the Word tyranny
From
Greek
 = tyrannos = tyrant =
master, sovereign, lord, absolute
ruler
= tyrannos = tyrant =
master, sovereign, lord, absolute
ruler
Examples of Tyrannies in History
The
term tyrant can refer to a
cruel, oppressive, or unjust ruler.
Or it can refer to someone who rules
without having the legal right to do
so, an usurper. Or it can refer to
both, of course.
 Dionysius I
the Elder made
himself tyrant of Syracuse in 405
BC.
Dionysius I
the Elder made
himself tyrant of Syracuse in 405
BC.
Should you decide to kill a tyrant,
you will commit tyrannicide. |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
Go here for all
 Governments in History.
Governments in History.
More History
|
| |
Browse the Dictionary:
 History Dictionary A - F
History Dictionary A - F
 History
Dictionary G - Z
History
Dictionary G - Z






Famous Speeches in History
Browse the speech archive:
 Speeches by Topic A-Z
Speeches by Topic A-Z
 Speeches by Speaker A-Z
Speeches by Speaker A-Z
 Speeches in Chronological
Order
Speeches in Chronological
Order
 Speeches Given by Women
Speeches Given by Women
 Speeches Given by African-Americans
Speeches Given by African-Americans
 Speeches Given by U.S. Presidents
Speeches Given by U.S. Presidents


There is danger from all men. The only maxim of
a free government ought to
be to trust no man living with power to endanger the public liberty.
John Adams,
1772
Greco-Persian Wars
Also called the
Persian Wars, the Greco-Persian Wars were
fought for almost half a century from 492 to
449 BC. Greece won against enormous odds. Here
is more:
 Battle of Marathon
Battle of Marathon
 Battle of Thermopylae
Battle of Thermopylae
 Battle of Salamis
Battle of Salamis
 Battle of Plataea
Battle of Plataea
They that are discontented
under monarchy, call it tyranny; and they that are displeased with
aristocracy, call it oligarchy: so also, they which find themselves grieved
under a democracy, call it anarchy, which signifies the want of government;
and yet I think no man believes, that want of government, is any new kind of
government.
Thomas Hobbes, Leviathan, 1651

The Divine Almanac
Who all roamed the heavens in
olden times? The Who's Who of
ancient gods.
 Check out
the Divine Almanac
Check out
the Divine Almanac


Where some people are very
wealthy and others have nothing, the result will be either extreme democracy
or absolute oligarchy, or despotism will come from either of those excesses.
Aristotle (384-322 BC) in Politics
|
|